Micromate™ Case Report series presents real cases performed by the physicians currently using the world’s smallest robot for percutaneous procedures.
Today, we join Dr. Marco van Strijen, Interventional Radiologist at the St. Antonius Hospital, for a robot-guided parotid gland biopsy.
Clinical Context
The patient was an 82-year-old female exhibiting facial pain. The MRI scan showed potential nerve-vessel conflict along the trigeminal nerve. A homogeneous mass, potentially originated from the left parotid gland, has been incidentally found in a deep location with the scan, but was invisible under ultrasound.
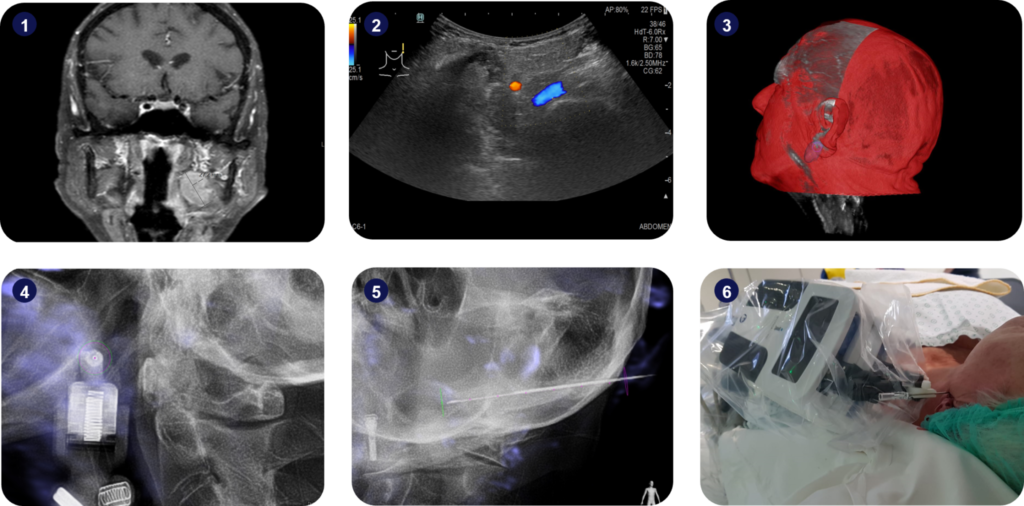
1) Homogenous mass with 27.2mm of diameter found on the MRI scan; 2) The lesion was not visible under ultrasound imaging; 3) Segmentation of the lesion (in purple), based on the fused intra-operative 3D scan and pre-operative MRI scan; 4) Alignment of Micromate™ to the surgical plan under live imaging; 5) Insertion of the guidance needle and tissue harvesting; 6) Setup picture.
Interventional Procedure
An intra-operative 3D scan of the patient in supine position was performed using a Philips Allura Xper FD20 angiography device and fused with the pre-operative MRI scan. To allow an unimpeded robotic approach, a strong emphasis was given to patient positioning by using a vacuum cushion to limit potential patient motion during the procedure and ensure the extension of the neck. The suspicious lesion was segmented, and the surgical trajectory was planned using the Xper Guide planning software. The target point for the insertion of the biopsy needle had been defined at the distal border of the segmented lesion, to ensure tissue harvesting covered the whole lesion.
Micromate™ was then gross-positioned near the predefined entry-point and remotely controlled for alignment to the surgical plan under fluoroscopic live imaging. After the robotic alignment, an 18G biopsy needle was coaxially inserted twice through a 17G guiding needle for tissue harvesting. An apocrine metaplasia was diagnosed, with no dysplasia, inflammation, or malignancy. The procedure lasted 17 minutes and the patient had no complications. Post-operative accuracy measurements indicated a trajectory alignment accuracy of 0.0mm on the Entry Point View, an angular displacement of 0.9 degrees along the trajectory in the Progress View, and a needle tip accuracy of 0.02mm.
Key Takeaways
Micromate™ helped the clinical team achieve submillimeter accuracy during a biopsy on a delicate anatomy, essential for an accurate diagnosis.
Adequate patient positioning is paramount for an accurate and safe robotic execution of a surgical trajectory. Using a vacuum cushion limits patient motion during the intervention and allows Micromate™ to achieve submillimeter accuracy.