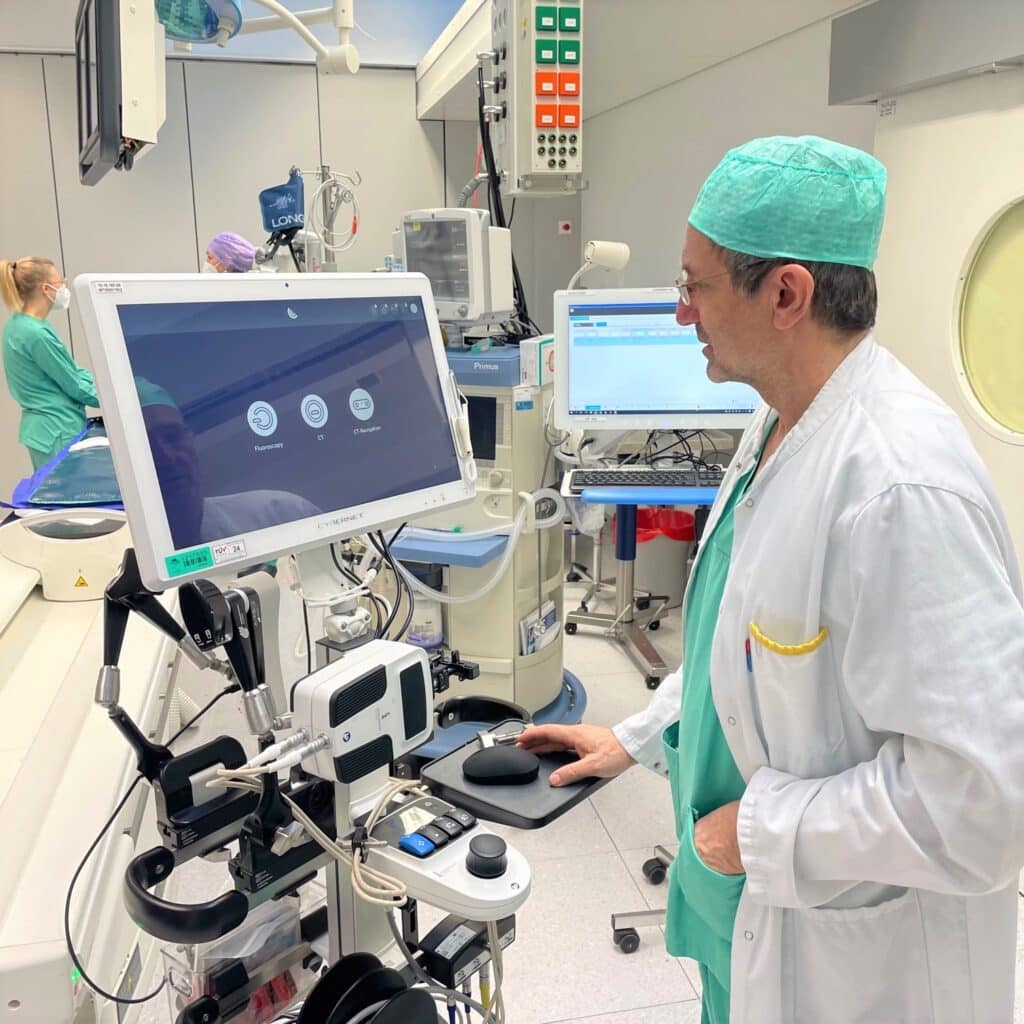
This time last year, we announced our Micromate’s new planning and navigation station, which made our needle-based intervention miniature robot available for use with CT scanners.
The first cases happened later in 2022 at the St. Antonius Hospital in the Netherlands, and since then, more hospitals have adopted the robotic system in their CT-guided procedures.
Today, we take a look back at the successful first cases in four different hospitals.
St. Antonius Hospital, The Netherlands | Dr. Marco van Strijen
Procedures: Biopsies of the Lung, Spleen, and Pelvic Bone; 100% diagnostic yield.
Key takeaway: The system’s small footprint and navigated alignment allowed the physician to replicate his CBCT workflow in the CT room, with planning scans being done with the robot in place and only one to no scans needed during needle insertion.
University General Hospital “ATTIKON”, Greece | Dr. Dimitrios Filippiadis
Procedures: Biopsies of the Liver, Pancreas, and Pelvic Bone; 100% diagnostic yield.
Key takeaway: The system integrated seamlessly into the clinical workflow, allowing the physician to replicate the usual freehand CT workflow, now with assistance of robotic guidance and navigation. This was also his first time using the robot, attesting to its ease of use and fast learning curve.
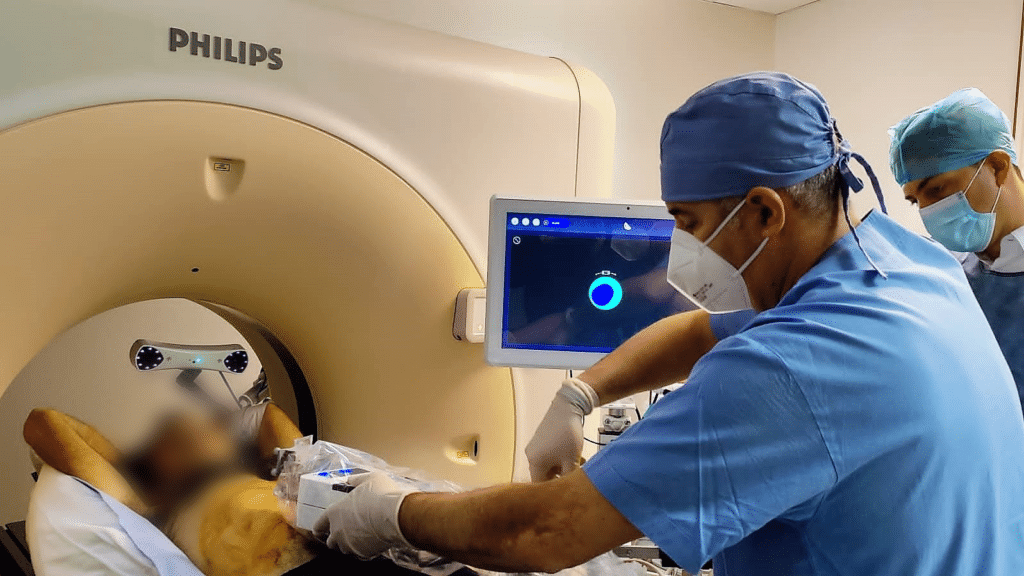
Ordensklinikum Linz, Austria | Dr. Alexander Kupferthaler
Procedure: Microwave Ablation of the Liver
Key takeaway: The system enabled the precise positioning of the ablation probe off-plane from an oblique angle, providing stable guidance to reach a challenging target without requiring needle repositioning or significant changes to the standard ablation workflow.
Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria | Dr. Reto Bale
Procedure: Targeted drug delivery
Key takeaway: The system provided angular accuracy in targeting the sphenopalatine ganglion through a narrow path with 2.82 by 6.18 by 3.15 mm, enabling the delivery of 50 IU of botulinum toxin type A in a patient with chronic cluster headaches.